What is Oxymatrine used for?
2023-12-11 14:38:50
 Oxymatrine powder is an herbal extract that comes from the root of Sophora flavescens, a plant common in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Oxymatrine has been used medicinally in China for nearly 2,000 years for its broad therapeutic benefits (1).
Oxymatrine powder is an herbal extract that comes from the root of Sophora flavescens, a plant common in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). Oxymatrine has been used medicinally in China for nearly 2,000 years for its broad therapeutic benefits (1).
In recent decades, oxymatrine has attracted increased interest from Western medicine due to emerging scientific research verifying many of its traditional therapeutic properties. Studies show that oxymatrine may help fight cancer, viral infections, inflammation, allergies, and more (2).
So what exactly is oxymatrine used for when it comes to health and healing? Here’s an overview of the current scientific research behind oxymatrine’s many medicinal uses.
1.  Fighting Cancer and Tumors
Fighting Cancer and Tumors
A significant amount of recent research has focused on oxymatrine's anti-cancer abilities, with over 180 related studies in the past decade. In vitro and animal studies show oxymatrine can inhibit the growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis of many types of cancer cells (3).
Specific cancers where oxymatrine demonstrates anti-tumor abilities include:
 - Pancreatic cancer: Oxymatrine was shown to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (4).
- Pancreatic cancer: Oxymatrine was shown to induce apoptosis and cell cycle arrest (4).
- Breast cancer: Oxymatrine may overcome drug resistance and radiation resistance (5).
- Colon cancer: The extract suppressed colon cancer cell proliferation and triggered programmed cell death (6).
- Liver cancer: Oxymatrine exhibited cytotoxicity towards hepatocellular carcinoma cells (7).
- Lung cancer: Studies show the compound inhibited migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions
of cells (8).
The anti-cancer mechanisms behind oxymatrine are multi-targeted and complex. But essentially, the extract
regulates gene expression levels and alters important signaling pathways within cancer cells, stopping them from
growing and spreading (2).
While most research is still preliminary, oxymatrine shows immense promise as an integrative treatment
alongside conventional liver, breast, colon, lung, pancreas and other cancer therapies.
2. Fighting Viruses
Oxymatrine demonstrates broad antiviral activities against an array of viruses through several mechanisms. It directly kills viral cells, inhibits viral replication, and enhances immunity against viruses.
Specific viruses oxymatrine shows effectiveness against include:
 - Hepatitis B virus (HBV): Oxymatrine suppressed HBV replication in vitro and improved hepatitis B symptoms in combination with standard drug therapy in human studies.
- Hepatitis B virus (HBV): Oxymatrine suppressed HBV replication in vitro and improved hepatitis B symptoms in combination with standard drug therapy in human studies.
- Coxsackievirus B3 (CVB3): Oxymatrine protected against myocarditis and heart injury from viral infection in mice.
- Respiratory viruses: Test-tube studies found oxymatrine has antiviral effects on parainfluenza, RSV, and several flu viruses.
- Herpes simplex virus (HSV): Topical oxymatrine cured skin lesions from HSV-1 in an animal model.
- HIV: Though research is limited, one study showed oxymatrine may inhibit HIV proliferation.
The antiviral properties of oxymatrine make it potentially useful for a wide variety of viral infectious diseases. More clinical trials are still needed, but current evidence verifies its traditional use against hepatitis B along with other viral infections.
3. Regulating Immune Function and Reducing Inflammation
Excess inflammation underlies modern inflammatory disorders like heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), eczema, asthma and more. Oxymatrine appears to regulate overactive immune responses that drive unnecessary inflammation.
Animal research found oxymatrine effectively reduced inflammation in models of:
 - Pancreatitis: Protected against inflammatory damage and pancreatic cell injury.
- Pancreatitis: Protected against inflammatory damage and pancreatic cell injury.
- Heart injury: Decreased myocardial inflammation from ischemia-reperfusion.
- Liver injury: Relieved inflammatory hepatitis in mice.
- Lung injury: Attenuated inflammatory damage and rebuilt alveolar structure after insult.
- Kidney inflammation: Significantly inhibited local cytokine release and tissue damage.
- Skin inflammation: Oxymatrine ointments eased inflammation in eczema models.
The anti-inflammatory effects of oxymatrine are likely due to inhibition of some pro-inflammatory cytokines,
immune cell activation, NF-κB signaling and more.
By calming excessive immune reactions, oxymatrine shows promise for managing modern inflammatory-based
disorders. Its immune-modulating abilities may also help fight allergies and asthma.
4. Protecting Liver Health
The liver detoxifies your blood, metabolizes nutrients, secretes bile, and performs other vital roles related to digestion and metabolism. Oxymatrine has been used traditionally to heal liver issues and modern research confirms potent hepatoprotective effects.
In both human and animal studies, oxymatrine:
- Protects liver cells from chemical toxin damage.
- Suppresses fibrosis and cirrhosis development.
- Aids recovery of liver function in hepatitis patients.
- Reduces fatty liver caused by alcohol, poor diet or diabetes.
The mechanisms behind its beneficial effects on liver health are multi-faceted. 98% Oxymatrine demonstrates direct antioxidant abilities, enhances activity of liver antioxidant enzymes, reduces liver cell apoptosis, protects mitochondria and more.
The research clearly supports the traditional use of oxymatrine supplements to improve liver health, treat disease, and prevent damage from toxins or medications.
What is the CAS number of Oxymatrine?
The CAS registry number, also known as CAS number or CAS RN, is a unique numerical identifier assigned to every chemical substance described in scientific literature. CAS stands for Chemical Abstracts Service, the organization that manages the database of chemical substances and assigns these identifiers. The CAS registry now consists of over 154 million organic and inorganic substances and over 80 million protein and DNA sequences.
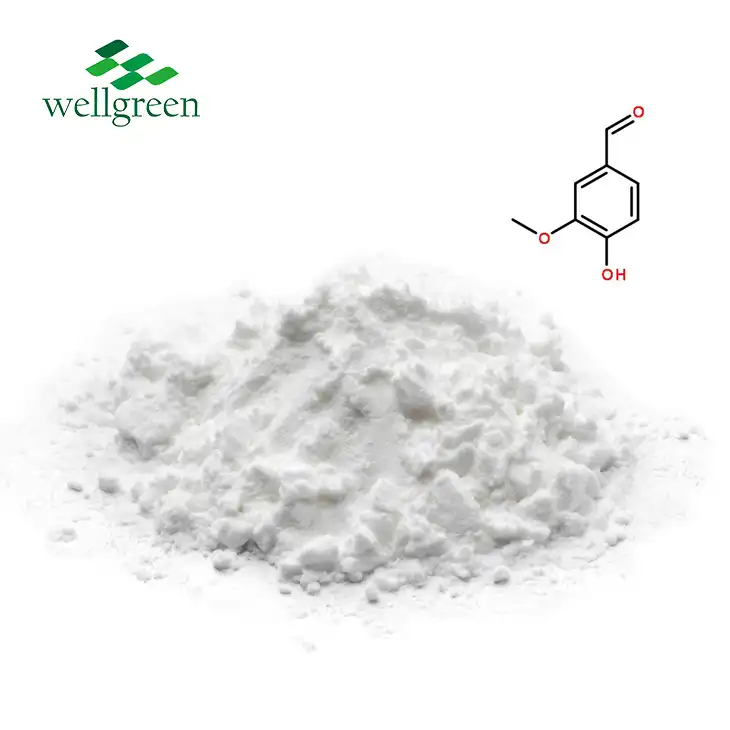
For oxymatrine, the CAS number is 16837-52-8. This specific, unique number unambiguously identifies oxymatrine amidst the sea of over 154 million chemicals that currently have CAS numbers. The CAS number 16837-52-8 can be used to search databases and scientific literature to find information specifically on oxymatrine rather than any other matrine derivatives or confusingly similar chemical names.
Summary
 According to modern scientific investigation as well as nearly 2,000 years of traditional use in China, oxymatrine boasts an impressive array of therapeutic benefits:
According to modern scientific investigation as well as nearly 2,000 years of traditional use in China, oxymatrine boasts an impressive array of therapeutic benefits:
- Anti-cancer and anti-tumor abilities against liver, colon, breast, pancreatic and other cancer types.
- Antiviral effects against hepatitis B, coxsackie B virus, herpes, and more.
- Immune-regulating and anti-inflammatory properties that may help autoimmune conditions.
- Protects the liver from toxins, viruses, fatty buildup, and injury.
Other minor uses for oxymatrine include preventing cardiac arrhythmia, reducing pain, fighting fungi and bacteria, protecting kidneys, improving gastrointestinal disorders, and more.
Oxymatrine deserves further clinical evaluation to confirm therapeutic applications. But thus far, findings underscore this compound's immense medicinal value. Oxymatrine supplements may one day find regular use alongside prescription protocols for cancer, hepatitis, arthritis, and myriad other inflammation-driven diseases.
WELLGREEN is an innovation-driven manufacturer of herbal extracts since 2011 certified by ISO9001:2015, ISO22000, HALAL, KOSHER, HACCP, and Organic Certificate. If you need Oxymatrine powder, please contact us immediately, E-mail:wgt@allwellcn.com We can supply customized service as per your request.
References:
1. Lu YF, Wan J, Liu Y, Qi DW. Preparation and analgesic efficacy of oxymatrine microemulsion. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(9):1528-32.
2. Gao JL, Shi FD, Li ZH, et al. Advances in pharmacological activities and mechanisms of oxymatrine. Pharmazie. 2020;75(11):467-476.
3. Lu Y, Li CS, Qian LJ, et al. Oxymatrine induces human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells apoptosis via regulating expression of Bcl-2 and IAP families, and releasing of cytochrome C. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research. 2011;30:66.
4. Zhao XL, Wei L, Shi X, et al. Oxymatrine induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation of human pancreatic cancer cells via mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. World J Surg Oncol. 2017;15(1):12.
5. Wu XZ, Chen D. Effectiveness of oxymatrine in treatment of cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016;37(10):1194-1206.
6. Guo QL, You QD, Wu ZQ, Yuan ST, Zhao L. General pharmacological study on anti-inflammatory and analgesic actions of oxymatrine. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica. 2004;29:32–34
7. Fan J, Wu XZ, Zhang SL, Li XJ, Wang XY, Xiang GL. Oxymatrine induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis and suppresses cell adhesion, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(2):1719-1724.
8. Wu D, Dou J, Gu N, et al. Oxymatrine inhibits glioma cell growth through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Oncol Lett. 2013;5(1):199-203.
9. Gao JL, Shi FD, Li ZH, et al. Advances in pharmacological activities and mechanisms of oxymatrine. Pharmazie. 2020;75(11):467-476.






